記事は長いです、が作りました。
はじめに
「地震速報を、自宅で即座に音と画面で受け取りたい」。そんな動機から、Raspberry Pi 2とe-ink(電子ペーパー)ディスプレイを使った防災・生活情報ボードを自作しました。
普段は時計、天気予報、鉄道の運行情報を常時表示し、緊急地震速報(EEW)を検知した瞬間にアラート音を鳴らして画面を切り替える。e-inkの「常時表示・低消費電力」という特性を活かした実用的なシステムです。
この記事では、構想からハマりポイントの解決までを時系列で紹介します。

システム概要
全体構成
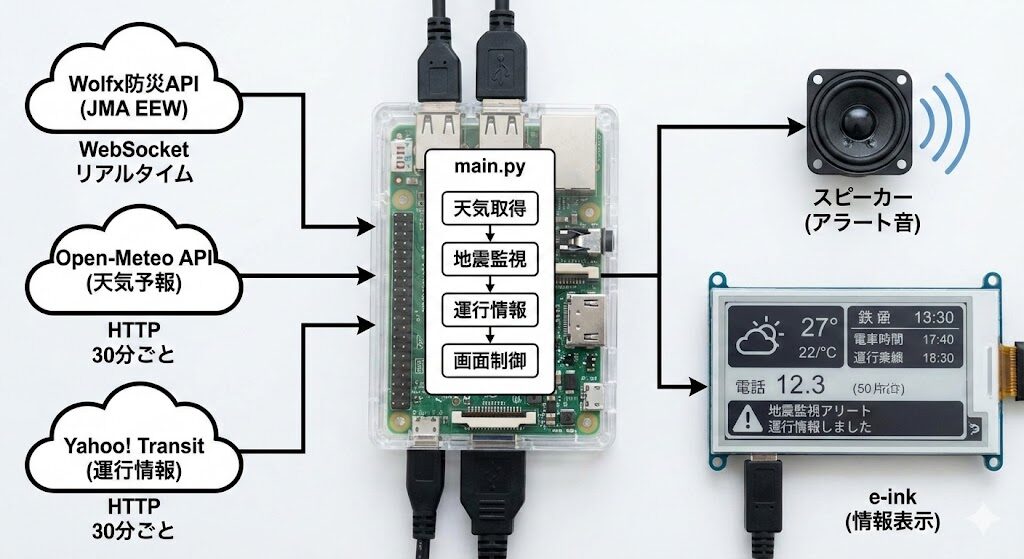
ハイブリッドアラートの設計思想
e-inkディスプレイの画面書き換えには1〜3秒かかります。緊急地震速報の秒数カウントダウンのような超リアルタイム表示には向きません。そこで以下のハイブリッド構成を採用しました。
EEW検知 → 即座にスピーカーからアラート音(遅延0秒)
→ 同時にe-inkの書き換えをスタート(1〜3秒後に完了)
音の役割:「何か来た!」と身構える
画面の役割:「いつ・どこ・いくつ」の詳細確認
通常時の画面レイアウト
こんなイメージです。

ハードウェア構成
| コンポーネント | 仕様 |
|---|---|
| 本体 | Raspberry Pi 2(900MHz ARM, 1GB RAM) |
| ディスプレイ | Waveshare 2.7inch e-Paper HAT V2(264×176, 白黒, 4階調対応) |
| オーディオ出力 | オンボード3.5mmステレオミニジャック → スピーカー |
| ネットワーク | LANケーブル接続(Pi 2にはWi-Fi非搭載) |
e-Paper HAT V2の基板設定
V2モデルではConfig/BSスイッチを「0」側(4-wire SPI)に設定し、基板上の0Ω抵抗が「4-wire SPI」側に実装されていることを確認しています。
GPIOピン配置
| 用途 | GPIOピン (BCM) |
|---|---|
| SPI: RST | 17 |
| SPI: DC | 25 |
| SPI: CS | 8 |
| SPI: BUSY | 24 |
| Button 1 | 5 |
| Button 2 | 6 |
| Button 3 | 13 |
| Button 4 | 19 |
ボタンのGPIO番号は、後述のgpio_scan.pyで実機確認しました。
ソフトウェア環境のセットアップ
OS・基本設定
- Raspberry Pi OS(Debian Bookworm)
- SPI有効化済み(
/dev/spidev0.0)
パッケージインストール
# Pythonライブラリ
pip install waveshare-epd websockets requests beautifulsoup4 --break-system-packages
# 日本語フォント
sudo apt-get install fonts-noto-cjk -y
# アラート音生成ツール
sudo apt-get install sox -y
NTP時刻同期
sudo timedatectl set-ntp true
sudo timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Tokyo
/etc/systemd/timesyncd.conf に日本のNTPサーバーを指定:
[Time]
NTP=ntp.nict.jp time.google.com
FallbackNTP=ntp.ubuntu.com
実装ステップ①:Wolfx WebSocket APIの接続確認
最初の一歩として、Raspberry Pi 2からWolfx防災APIに接続できることをCLIで確認しました。
Wolfx防災APIの概要
- 無料・認証不要のWebSocket API
- JMA緊急地震速報をリアルタイムプッシュ配信
- エンドポイント:
wss://ws-api.wolfx.jp/jma_eew - サーバーは接続時と以降毎分、heartbeatを送信
- クライアントからのping返信は推奨(必須ではない)
利用規約により、過剰な接続数の生成と二次API構築は禁止。人間向けの情報発信は許可されています。
CLIテストスクリプト
wolfx_test.pyとして作成:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""Wolfx JMA EEW WebSocket CLI検証スクリプト"""
import asyncio
import json
import websockets
ENDPOINT = "wss://ws-api.wolfx.jp/jma_eew"
async def connect():
print(f"[*] Connecting to {ENDPOINT} ...")
async with websockets.connect(ENDPOINT) as ws:
print("[+] Connected.")
while True:
try:
raw = await ws.recv()
print(f"\n[{asyncio.get_event_loop().time():.1f}s] Raw: {raw}")
try:
data = json.loads(raw)
print(f" Parsed: {json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}")
except json.JSONDecodeError:
print(f" (JSON以外のパケット)")
# heartbeat返信
if isinstance(data, dict) and data.get("type") == "heartbeat":
await ws.send("ping")
print(" -> ping送信")
except websockets.exceptions.ConnectionClosed as e:
print(f"[-] Connection closed: {e}")
break
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(connect())
実行結果
[*] Connecting to wss://ws-api.wolfx.jp/jma_eew ...
[+] Connected.
[1419.1s] Raw: {"type":"heartbeat","ver":18,"id":"d697cc0d054e16e2","timestamp":1769926086354}
Parsed: {
"type": "heartbeat",
...
}
-> ping送信
[1419.2s] Raw: {"type":"pong","timestamp":1769926086373}
Parsed: {
"type": "pong",
"timestamp": 1769926086373
}
heartbeat → ping → pong が約60秒間隔で安定動作。Pi 2でも問題なくWebSocket接続が維持できることを確認しました。
ハマりポイント:heartbeatの判定
当初、if raw == "heartbeat" と文字列比較していましたが、実際にはJSON形式 {"type":"heartbeat",...} で送信されます。正しくは data.get("type") == "heartbeat" でJSONパース後に判定する必要がありました。
実装ステップ②:天気アイコンの自作
e-inkは白黒2値なので、PILで32×32のモノクロBMP画像を生成しました。
アイコン生成スクリプト
create_icons.py:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import math
def create_weather_icons():
"""天気アイコンを生成(32x32サイズ、白黒2値)"""
icon_dir = './weather_icons'
size = (32, 32)
# 1. 晴れ(太陽)
img = Image.new('1', size, 255)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
draw.ellipse([10, 10, 22, 22], fill=0, outline=0)
for angle in range(0, 360, 45):
rad = math.radians(angle)
x1 = 16 + int(12 * math.cos(rad))
y1 = 16 + int(12 * math.sin(rad))
x2 = 16 + int(16 * math.cos(rad))
y2 = 16 + int(16 * math.sin(rad))
draw.line([x1, y1, x2, y2], fill=0, width=2)
img.save(f'{icon_dir}/sunny.bmp')
print("Created: sunny.bmp")
# 2. くもり(雲)
img = Image.new('1', size, 255)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
draw.ellipse([6, 12, 16, 22], fill=0, outline=0)
draw.ellipse([14, 10, 24, 20], fill=0, outline=0)
draw.ellipse([20, 14, 28, 24], fill=0, outline=0)
draw.rectangle([6, 18, 28, 24], fill=0, outline=0)
img.save(f'{icon_dir}/cloudy.bmp')
print("Created: cloudy.bmp")
# 3. 雨(雲+雨粒)
img = Image.new('1', size, 255)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
draw.ellipse([6, 6, 14, 14], fill=0, outline=0)
draw.ellipse([12, 4, 20, 12], fill=0, outline=0)
draw.ellipse([18, 6, 26, 14], fill=0, outline=0)
draw.rectangle([6, 10, 26, 14], fill=0, outline=0)
for x in [10, 16, 22]:
draw.line([x, 16, x-2, 28], fill=0, width=2)
img.save(f'{icon_dir}/rainy.bmp')
print("Created: rainy.bmp")
# 4. 雪(雲+雪の結晶)
img = Image.new('1', size, 255)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
draw.ellipse([6, 2, 14, 10], fill=0, outline=0)
draw.ellipse([12, 0, 20, 8], fill=0, outline=0)
draw.ellipse([18, 2, 26, 10], fill=0, outline=0)
draw.rectangle([6, 6, 26, 10], fill=0, outline=0)
for x, y in [(10, 20), (22, 20), (16, 28)]:
draw.text((x-3, y-4), "*", fill=0)
img.save(f'{icon_dir}/snowy.bmp')
print("Created: snowy.bmp")
if __name__ == "__main__":
create_weather_icons()
print("All icons created.")
mkdir -p weather_icons
python3 create_icons.py
実装ステップ③:GPIOボタンの特定
Waveshare 2.7inch HAT V2には4つのボタンがありますが、公式ドキュメントだけでは不安だったので、テストスクリプトで実機確認しました。
GPIOスキャンスクリプト
gpio_scan.py:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""GPIO Button Scanner - ボタンのGPIO番号を特定"""
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
# 候補となるGPIOピン
CANDIDATE_PINS = [5, 6, 13, 16, 19, 20, 21, 26]
def main():
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
for pin in CANDIDATE_PINS:
GPIO.setup(pin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
prev_states = {pin: GPIO.HIGH for pin in CANDIDATE_PINS}
print("=== GPIO Button Scanner ===")
print(f"Monitoring GPIOs: {CANDIDATE_PINS}")
print("Press buttons on the HAT to detect which GPIO they use.")
print("Press Ctrl+C to exit.\n")
try:
while True:
for pin in CANDIDATE_PINS:
current = GPIO.input(pin)
if current != prev_states[pin]:
if current == GPIO.LOW:
print(f">>> GPIO {pin}: BUTTON PRESSED (HIGH -> LOW)")
else:
print(f">>> GPIO {pin}: BUTTON RELEASED (LOW -> HIGH)")
prev_states[pin] = current
time.sleep(0.05)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\nScan finished.")
finally:
GPIO.cleanup()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
実行してボタン1〜4を順番に押した結果、GPIO 5, 6, 13, 19に対応していることが確認できました。
実装ステップ④:アラート音の準備
オーディオデバイスの確認
当初 raspi-config で「No internal audio devices found」と表示されましたが、aplay -lで確認したところ、card 1(bcm2835 Headphones)が利用可能でした。
# デフォルトデバイスの設定
cat > ~/.asoundrc << 'EOF'
pcm.!default {
type plug
slave.pcm "hw:1,0"
}
ctl.!default {
type hw
card 1
}
EOF
アラート音の生成
# 16-bit形式で断続的な警告音を生成(0.3秒ON / 0.1秒OFF × 8回)
sox -n -r 44100 -b 16 alert.wav synth 0.3 sine 2000 : synth 0.1 sine 0 repeat 7
# テスト再生
aplay alert.wav
ハマりポイント:32-bit WAVが再生できない
soxのデフォルトで32-bit形式が生成され、bcm2835 Headphonesでは再生できませんでした。このデバイスはU8(8-bit)とS16_LE(16-bit)のみ対応しているため、-b 16 を明示する必要がありました。

実装ステップ⑤:メインプログラム
ここまでの要素をすべて統合した main.py の全体です。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
地震早期警報 + 天気 + 運行情報 表示システム
Raspberry Pi 2 + Waveshare 2.7inch e-Paper HAT V2
"""
import threading
import time
import json
import subprocess
import traceback
from datetime import datetime
import requests
import websocket
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from waveshare_epd import epd2in7_V2 # 必ず V2 を指定
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
# ============================================================
# グローバル変数
# ============================================================
earthquake_alert = False
earthquake_alert_time = 0
earthquake_data = {}
weather_icons = {}
weather_data = None
train_status_data = None
last_update = 0
last_weather_fetch = 0
last_train_fetch = 0
force_update = False
# ============================================================
# 定数
# ============================================================
# ボタンのGPIO番号(gpio_scan.pyで確認済み)
BUTTON_1 = 5 # 手動更新
BUTTON_2 = 6 # 通常画面に戻る
BUTTON_3 = 13 # アラート音テスト
BUTTON_4 = 19 # テストEEW表示
# アラート設定
USE_BUZZER = False # True: GPIOブザー, False: スピーカー
BUZZER_PIN = 12
# ポーリング用
DEBOUNCE_TIME = 0.3
button_prev_states = {BUTTON_1: 1, BUTTON_2: 1, BUTTON_3: 1, BUTTON_4: 1}
button_last_press_time = {BUTTON_1: 0, BUTTON_2: 0, BUTTON_3: 0, BUTTON_4: 0}
# ============================================================
# 天気関連
# ============================================================
def weather_code_to_icon(code):
"""WMO Weather codeをアイコン名に変換"""
if code in [0, 1, 2, 3]:
return 'sunny'
elif code in [45, 48]:
return 'cloudy'
elif code in [51, 53, 55, 61, 63, 65, 80, 81, 82]:
return 'rainy'
elif code in [71, 73, 75]:
return 'snowy'
else:
return 'cloudy'
def weather_code_to_text(code):
"""WMO Weather codeを日本語テキストに変換"""
codes = {
0: "快晴", 1: "晴れ", 2: "晴れ", 3: "晴れ",
45: "霧", 48: "霧",
51: "小雨", 53: "雨", 55: "大雨",
61: "小雨", 63: "雨", 65: "大雨",
71: "小雪", 73: "雪", 75: "大雪",
80: "にわか雨", 81: "にわか雨", 82: "豪雨",
95: "雷雨", 96: "雷雨", 99: "雷雨"
}
return codes.get(code, "不明")
def load_weather_icons():
"""天気アイコンを読み込み"""
icons = {}
icon_dir = '/home/taka/earthquake_display/weather_icons'
for name in ['sunny', 'cloudy', 'rainy', 'snowy']:
try:
icons[name] = Image.open(f'{icon_dir}/{name}.bmp')
print(f"Loaded icon: {name}")
except Exception:
icons[name] = Image.new('1', (32, 32), 255)
return icons
def fetch_hourly_weather(lat, lon):
"""Open-Meteo APIから1時間ごとの天気予報を取得"""
url = "https://api.open-meteo.com/v1/forecast"
params = {
"latitude": lat,
"longitude": lon,
"hourly": "temperature_2m,precipitation_probability,weathercode",
"timezone": "Asia/Tokyo",
"forecast_days": 2 # 日付またぎ対応のため2日分取得
}
response = requests.get(url, params=params, timeout=10)
return response.json()
# ============================================================
# 運行情報
# ============================================================
def fetch_train_status(url):
"""Yahoo!路線情報から運行状況を取得"""
try:
resp = requests.get(url, timeout=10)
resp.encoding = resp.apparent_encoding
if resp.status_code != 200:
return None, "接続エラー"
soup = BeautifulSoup(resp.content, 'html.parser')
status_div = soup.find('div', id='mdServiceStatus')
if not status_div:
return None, "取得失敗"
# dt要素で判定
dt_elem = status_div.find('dt')
if dt_elem and "平常運転" in dt_elem.get_text(strip=True):
return True, "平常運転"
# dd要素のクラスで判定
dd_elem = status_div.find('dd')
if dd_elem:
classes = dd_elem.get('class', [])
if 'normal' in classes:
return True, "平常運転"
elif 'trouble' in classes:
return False, "遅延"
return None, "不明"
except requests.Timeout:
return None, "タイムアウト"
except Exception as e:
print(f"Train status error: {e}")
traceback.print_exc()
return None, "エラー"
def fetch_all_train_status():
"""運行情報を取得(路線は環境に合わせて変更)"""
# 例:JR埼京線
url_saikyo = "https://transit.yahoo.co.jp/diainfo/50/0"
is_ok, text = fetch_train_status(url_saikyo)
return {
'saikyo': {'ok': is_ok, 'text': text}
}
# ============================================================
# 画面描画
# ============================================================
def draw_normal_screen(epd, weather_data, icons, train_data=None):
"""通常時の画面描画(天気+運行情報)"""
image = Image.new('1', (epd.height, epd.width), 255)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
# フォント設定(日本語対応)
try:
font_large = ImageFont.truetype(
'/usr/share/fonts/opentype/noto/NotoSansCJK-Bold.ttc', 20, index=0)
font_medium = ImageFont.truetype(
'/usr/share/fonts/opentype/noto/NotoSansCJK-Regular.ttc', 14, index=0)
font_small = ImageFont.truetype(
'/usr/share/fonts/opentype/noto/NotoSansCJK-Regular.ttc', 11, index=0)
except Exception:
font_large = ImageFont.load_default()
font_medium = ImageFont.load_default()
font_small = ImageFont.load_default()
now = datetime.now()
# --- 上段:時計+現在の天気 ---
draw.text((5, 5), now.strftime("%H:%M"), font=font_large, fill=0)
draw.text((5, 30), now.strftime("%m/%d (%a)"), font=font_medium, fill=0)
hourly_times = weather_data['hourly']['time']
hourly_temps = weather_data['hourly']['temperature_2m']
hourly_precip = weather_data['hourly']['precipitation_probability']
hourly_weather = weather_data['hourly']['weathercode']
# 現在時刻に最も近いインデックスを見つける(日付またぎ対応)
current_index = None
min_diff = float('inf')
for i, time_str in enumerate(hourly_times):
time_obj = datetime.fromisoformat(time_str)
diff = abs((time_obj - now).total_seconds())
if diff < min_diff:
min_diff = diff
current_index = i
if current_index is not None:
current_temp = hourly_temps[current_index]
current_precip = hourly_precip[current_index] or 0
current_weather_code = hourly_weather[current_index]
current_weather = weather_code_to_text(current_weather_code)
current_icon = weather_code_to_icon(current_weather_code)
icon_img = icons.get(current_icon)
if icon_img:
image.paste(icon_img, (110, 5))
draw.text((145, 5), current_weather, font=font_medium, fill=0)
draw.text((145, 24), f"{current_temp:.0f}°C", font=font_medium, fill=0)
draw.text((220, 5), f"{current_precip:.0f}%", font=font_small, fill=0)
# 区切り線
draw.line((0, 55, 264, 55), fill=0, width=1)
# --- 中段:4時間分の予報 ---
x_positions = [5, 68, 132, 196]
for i in range(4): # 0〜3時間後
if current_index is not None and current_index + i < len(hourly_times):
future_index = current_index + i
future_time = datetime.fromisoformat(hourly_times[future_index])
future_temp = hourly_temps[future_index]
future_precip = hourly_precip[future_index] or 0
future_weather_code = hourly_weather[future_index]
future_icon = weather_code_to_icon(future_weather_code)
x = x_positions[i]
draw.text((x, 60), future_time.strftime("%H:%M"), font=font_small, fill=0)
icon_img = icons.get(future_icon)
if icon_img:
small_icon = icon_img.resize((24, 24))
image.paste(small_icon, (x + 8, 78))
draw.text((x, 108), f"{future_temp:.0f}°C", font=font_small, fill=0)
draw.text((x, 128), f"{future_precip:.0f}%", font=font_small, fill=0)
# --- 下段:運行情報 ---
if train_data:
draw.line((0, 145, 264, 145), fill=0, width=1)
saikyo = train_data.get('saikyo', {})
saikyo_ok = saikyo.get('ok')
saikyo_text = saikyo.get('text', '不明')
if saikyo_ok is True:
mark = "●"
display_text = "平常"
elif saikyo_ok is False:
mark = "×"
display_text = saikyo_text
else:
mark = "?"
display_text = saikyo_text
draw.text((5, 150), f"埼京線 {mark} {display_text}", font=font_small, fill=0)
epd.display(epd.getbuffer(image))
def draw_earthquake_screen(epd, eq_data):
"""緊急地震速報画面"""
image = Image.new('1', (epd.height, epd.width), 255)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
try:
font_large = ImageFont.truetype(
'/usr/share/fonts/opentype/noto/NotoSansCJK-Bold.ttc', 20, index=0)
font_medium = ImageFont.truetype(
'/usr/share/fonts/opentype/noto/NotoSansCJK-Regular.ttc', 14, index=0)
except Exception:
font_large = ImageFont.load_default()
font_medium = ImageFont.load_default()
draw.text((10, 10), "緊急地震速報", font=font_large, fill=0)
draw.line((10, 35, 254, 35), fill=0, width=2)
draw.text((20, 45), f"震源:{eq_data.get('region', '不明')}", font=font_medium, fill=0)
draw.text((20, 70), f"M{eq_data.get('magnitude', '?')} "
f"深さ{eq_data.get('depth', '?')}km", font=font_medium, fill=0)
draw.text((20, 95), f"最大震度:{eq_data.get('max_intensity', '?')}",
font=font_medium, fill=0)
if 'origin_time' in eq_data:
draw.text((20, 120), f"発生:{eq_data['origin_time']}", font=font_medium, fill=0)
epd.display(epd.getbuffer(image))
# ============================================================
# アラート音
# ============================================================
def play_alert_buzzer(duration=3):
"""GPIOブザーでアラート音"""
try:
buzzer = GPIO.PWM(BUZZER_PIN, 2000)
buzzer.start(50)
end_time = time.time() + duration
while time.time() < end_time:
buzzer.ChangeDutyCycle(50)
time.sleep(0.3)
buzzer.ChangeDutyCycle(0)
time.sleep(0.1)
buzzer.stop()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Buzzer error: {e}")
def play_alert_sound():
"""スピーカーでアラート音を再生"""
try:
subprocess.Popen(
['aplay', '-D', 'plughw:1,0',
'/home/taka/earthquake_display/alert.wav'],
stdout=subprocess.DEVNULL, stderr=subprocess.DEVNULL)
print("Alert sound playing")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Audio playback error: {e}")
def play_alert():
"""アラート音を再生(別スレッドで実行)"""
if USE_BUZZER:
threading.Thread(target=play_alert_buzzer, args=(3,), daemon=True).start()
else:
threading.Thread(target=play_alert_sound, daemon=True).start()
# ============================================================
# WebSocket(地震監視)
# ============================================================
def earthquake_monitor():
"""Wolfx防災APIで地震情報を監視"""
global earthquake_alert, earthquake_alert_time, earthquake_data
def on_message(ws, message):
global earthquake_alert, earthquake_alert_time, earthquake_data
try:
data = json.loads(message)
msg_type = data.get('type', 'unknown')
print(f"Received: {msg_type}")
if msg_type == 'heartbeat':
ws.send("ping")
elif msg_type == 'jma_eew':
earthquake_alert = True
earthquake_alert_time = time.time()
earthquake_data = {
'region': data.get('Hypocenter', '不明'),
'magnitude': data.get('Magunitude', '?'),
'depth': data.get('Depth', '?'),
'max_intensity': data.get('MaxIntensity', '?'),
'origin_time': data.get('OriginTime', '')
}
print(f"EEW detected: {earthquake_data}")
play_alert()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Message parse error: {e}")
def on_error(ws, error):
print(f"WebSocket error: {error}")
def on_close(ws, close_status_code, close_msg):
print("WebSocket closed. Reconnecting in 10 seconds...")
time.sleep(10)
start_ws()
def on_open(ws):
print("WebSocket connected to Wolfx API")
def start_ws():
ws = websocket.WebSocketApp(
"wss://ws-api.wolfx.jp/jma_eew",
on_message=on_message,
on_error=on_error,
on_close=on_close,
on_open=on_open
)
ws.run_forever()
start_ws()
# ============================================================
# ボタン(ポーリング方式)
# ============================================================
def setup_buttons():
"""ボタンの初期化(ポーリング方式)"""
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
for i, button in enumerate([BUTTON_1, BUTTON_2, BUTTON_3, BUTTON_4], 1):
GPIO.setup(button, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
print(f"Button {i} (GPIO {button}) initialized for polling")
print("All buttons initialized (polling mode)")
def check_buttons():
"""ボタン状態を直接チェック(メインループ内で呼び出す)"""
global force_update, earthquake_alert, earthquake_alert_time, earthquake_data
current_time = time.time()
# Button 1: 手動更新
state1 = GPIO.input(BUTTON_1)
if state1 == GPIO.LOW and button_prev_states[BUTTON_1] == GPIO.HIGH:
if current_time - button_last_press_time[BUTTON_1] > DEBOUNCE_TIME:
print("Button 1 pressed: Force update")
force_update = True
button_last_press_time[BUTTON_1] = current_time
button_prev_states[BUTTON_1] = state1
# Button 2: 通常画面に戻る
state2 = GPIO.input(BUTTON_2)
if state2 == GPIO.LOW and button_prev_states[BUTTON_2] == GPIO.HIGH:
if current_time - button_last_press_time[BUTTON_2] > DEBOUNCE_TIME:
elapsed = current_time - earthquake_alert_time if earthquake_alert else 0
print(f"Button 2 pressed: Return to normal (after {elapsed:.0f}s)")
earthquake_alert = False
force_update = True
button_last_press_time[BUTTON_2] = current_time
button_prev_states[BUTTON_2] = state2
# Button 3: アラート音テスト
state3 = GPIO.input(BUTTON_3)
if state3 == GPIO.LOW and button_prev_states[BUTTON_3] == GPIO.HIGH:
if current_time - button_last_press_time[BUTTON_3] > DEBOUNCE_TIME:
print("Button 3 pressed: Alert test")
play_alert()
button_last_press_time[BUTTON_3] = current_time
button_prev_states[BUTTON_3] = state3
# Button 4: テストEEW
state4 = GPIO.input(BUTTON_4)
if state4 == GPIO.LOW and button_prev_states[BUTTON_4] == GPIO.HIGH:
if current_time - button_last_press_time[BUTTON_4] > DEBOUNCE_TIME:
print("Button 4 pressed: Test EEW")
earthquake_alert = True
earthquake_alert_time = time.time()
earthquake_data = {
'region': 'テスト震源',
'magnitude': '5.0',
'depth': '10',
'max_intensity': '4',
'origin_time': datetime.now().strftime('%H:%M:%S')
}
play_alert()
button_last_press_time[BUTTON_4] = current_time
button_prev_states[BUTTON_4] = state4
def setup_buzzer():
"""ブザーの初期化"""
if USE_BUZZER:
GPIO.setup(BUZZER_PIN, GPIO.OUT)
print(f"Buzzer initialized on GPIO {BUZZER_PIN}")
# ============================================================
# メインループ
# ============================================================
def main():
global weather_icons, weather_data, train_status_data
global last_update, last_weather_fetch, last_train_fetch, force_update
global earthquake_alert
# ボタン初期化(ポーリング方式)
print("Setting up buttons (polling mode)...")
setup_buttons()
print("Initializing e-Paper display...")
epd = epd2in7_V2.EPD()
epd.init()
epd.Clear()
print("Loading weather icons...")
weather_icons = load_weather_icons()
setup_buzzer()
print("Starting earthquake monitor...")
threading.Thread(target=earthquake_monitor, daemon=True).start()
last_update = 0
last_weather_fetch = 0
last_train_fetch = 0
try:
while True:
check_buttons()
current_time = time.time()
# --- 地震アラート優先 ---
if earthquake_alert:
elapsed = current_time - earthquake_alert_time
# 120秒で自動復帰
if elapsed > 120:
print(f"Auto-clearing earthquake alert after {elapsed:.0f}s")
earthquake_alert = False
force_update = True
else:
# 30秒ごとにカウントダウンログ
remaining = 120 - elapsed
if int(elapsed) % 30 == 0 and int(elapsed) > 0:
print(f"Earthquake alert active - "
f"auto-clear in {remaining:.0f}s")
draw_earthquake_screen(epd, earthquake_data)
time.sleep(0.1)
continue
# --- 天気データ取得(30分ごと) ---
if (current_time - last_weather_fetch > 1800
or last_weather_fetch == 0 or force_update):
try:
print("Fetching weather data...")
weather_data = fetch_hourly_weather(
lat=35.8792, lon=139.5197) # ふじみ野市
last_weather_fetch = current_time
print(f"Weather data fetched at "
f"{datetime.now().strftime('%H:%M:%S')}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Weather fetch error: {e}")
if weather_data is None:
force_update = False
time.sleep(0.1)
continue
# --- 運行情報取得(30分ごと) ---
if (current_time - last_train_fetch > 1800
or last_train_fetch == 0 or force_update):
try:
print("Fetching train status...")
train_status_data = fetch_all_train_status()
last_train_fetch = current_time
print(f"Train status fetched at "
f"{datetime.now().strftime('%H:%M:%S')}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Train status fetch error: {e}")
# --- 画面更新(60秒ごと) ---
if (current_time - last_update > 60
or last_update == 0
or force_update
or (weather_data is not None
and last_update < last_weather_fetch)):
if weather_data is not None:
try:
print("Drawing normal screen...")
draw_normal_screen(
epd, weather_data, weather_icons, train_status_data)
last_update = current_time
force_update = False
print(f"Display updated at "
f"{datetime.now().strftime('%H:%M:%S')}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Display update error: {e}")
force_update = False
time.sleep(0.1) # 100msごとにループ(ボタン応答性確保)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\nShutting down...")
print("Clearing display...")
epd.Clear()
GPIO.cleanup()
epd.sleep()
print("Display cleared and sleeping. Goodbye!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
ハマりポイント詳解:ボタンが全く反応しない問題
開発中に最も時間を使ったのがこの問題です。
現象
gpio_scan.py(前述のスクリプト)ではボタンが正常に検出できるのに、main.pyに組み込んだ途端、全ボタンが無反応になりました。
調査の過程
setup_buttons()内のGPIO.cleanup()がe-Paper HATのGPIO設定を消していた → 削除しても改善せず- ボタン初期化をe-Paper初期化の前に移動 → 改善せず
- sudoで実行 → 改善せず
- コールバック関数にデバッグprint追加 → 関数自体が呼ばれていない
根本原因
e-Paper HAT V2の初期化(epd.init())後、GPIO割り込み(GPIO.add_event_detect())が機能しなくなります。SPIドライバの初期化がGPIO割り込みシステムに影響を与えていると推定されます。
解決策
割り込みベースからポーリングベースに全面変更しました。gpio_scan.pyと同じ方式でGPIO状態を直接読み取ります。
# 割り込み方式(動かない)
GPIO.add_event_detect(BUTTON_1, GPIO.FALLING, callback=handler, bouncetime=300)
# ポーリング方式(動く)
state = GPIO.input(BUTTON_1)
if state == GPIO.LOW and prev_state == GPIO.HIGH:
# ボタン押下を検出
100msごとにメインループ内でチェックし、デバウンス処理(0.3秒のクールタイム)を入れています。
systemdによる自動起動
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/earthquake-display.service
[Unit]
Description=Earthquake Early Warning Display
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=taka
WorkingDirectory=/home/taka/earthquake_display
ExecStart=/usr/bin/python3 /home/taka/earthquake_display/main.py
Restart=always
RestartSec=10
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
sudo systemctl enable earthquake-display.service
sudo systemctl start earthquake-display.service
# ログ確認
journalctl -u earthquake-display.service -f
断念した機能:音声AI
Raspberry Pi 2に音声入力でAIに質問し、e-inkに回答を表示する機能を検討しましたが、見送りました。
Pi 2のスペック(900MHz ARM, 1GB RAM)ではローカルLLMの実行は不可能で、クラウドAPI経由であっても常時音声監視がCPUを圧迫し、地震速報の即応性を阻害するリスクがあったためです。Raspberry Pi 4以降で再検討する予定です。
得られた知見まとめ
| カテゴリ | 内容 |
|---|---|
| e-Paper HAT V2 | V1とV2でインポートモジュールが異なる。必ずepd2in7_V2を使う |
| GPIO割り込み | e-Paper HAT初期化後、add_event_detectが動作しなくなる。ポーリング方式で回避 |
| オーディオ | bcm2835 Headphonesは16-bit/8-bitのみ対応。32-bit WAVは再生不可 |
| 日本語表示 | Noto Sans CJK必須。.ttcファイルはindex=0指定が必要 |
| 天気API | forecast_days=1では日付またぎに対応できない。2日分取得する |
| WebSocket | heartbeatはJSON形式。文字列比較ではなくJSON解析が必要 |
| EEWタイプ | Wolfx APIのメッセージtypeはjma_eew(eewではない) |
| Webスクレイピング | Yahoo! TransitのHTML構造はHTMLファイル保存によるデバッグで特定 |
| 設計思想 | APIデータ取得と画面更新は異なる周期で分離すべき |
ファイル構成
/home/taka/earthquake_display/
├── main.py # メインプログラム
├── create_icons.py # アイコン生成スクリプト
├── alert.wav # 警告音(16-bit, 44100Hz)
├── gpio_scan.py # GPIOボタン特定用
├── wolfx_test.py # Wolfx API接続テスト用
└── weather_icons/
├── sunny.bmp # 晴れ(32×32)
├── cloudy.bmp # くもり
├── rainy.bmp # 雨
└── snowy.bmp # 雪
機能一覧
| 機能 | 説明 | 更新頻度 |
|---|---|---|
| 時計表示 | 現在時刻と日付 | 60秒 |
| 天気予報 | 現在天気+4時間先の予報(アイコン・気温・降水確率) | 30分 |
| 運行情報 | 鉄道の運行状況(Yahoo! Transit) | 30分 |
| 地震速報 | Wolfx APIからJMA緊急地震速報を受信・表示 | リアルタイム |
| アラート音 | 地震検知時にスピーカーで警告音 | 即時 |
| 自動復帰 | 地震画面を2分後に自動で通常画面に復帰 | – |
| ボタン1 | 手動で天気・運行情報を即座に更新 | 手動 |
| ボタン2 | 地震情報表示中に通常画面に戻る | 手動 |
| ボタン3 | アラート音テスト | 手動 |
| ボタン4 | テストEEW表示(開発用) | 手動 |
おわりに
Raspberry Pi 2という旧世代のハードウェアでも、リアルタイム防災システムは十分に構築できました。e-inkの「常時表示・低消費電力」という特性は、防災情報ボードに最適です。
開発中に最も学びが大きかったのは、e-Paper HAT初期化後にGPIO割り込みが死ぬ問題の特定と解決です。公式ドキュメントには記載がなく、テストスクリプトとの動作比較から切り分けていくしかありませんでした。同様の構成で開発する方の参考になれば幸いです。
今後の拡張候補として、Pi 4への移行による音声AI対応、より大きなe-inkディスプレイへの移行、震度に応じたアラート音の段階分けなどを検討しています。

